Semaglutide Weight Loss Dosage Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Semaglutide

Leah Bush
•
5 mins read
• Oct 3, 2024
Compounded Semaglutide is a popular medication used to support long-term weight management in adults, especially those dealing with obesity or weight-related health conditions like hypertension or type 2 diabetes. To achieve the best results and minimize side effects, it’s important to follow a carefully structured dosing schedule. This blog will guide you through the recommended dose escalation, maintenance strategies, and key considerations to help ensure safe and effective use of semaglutide for weight loss.
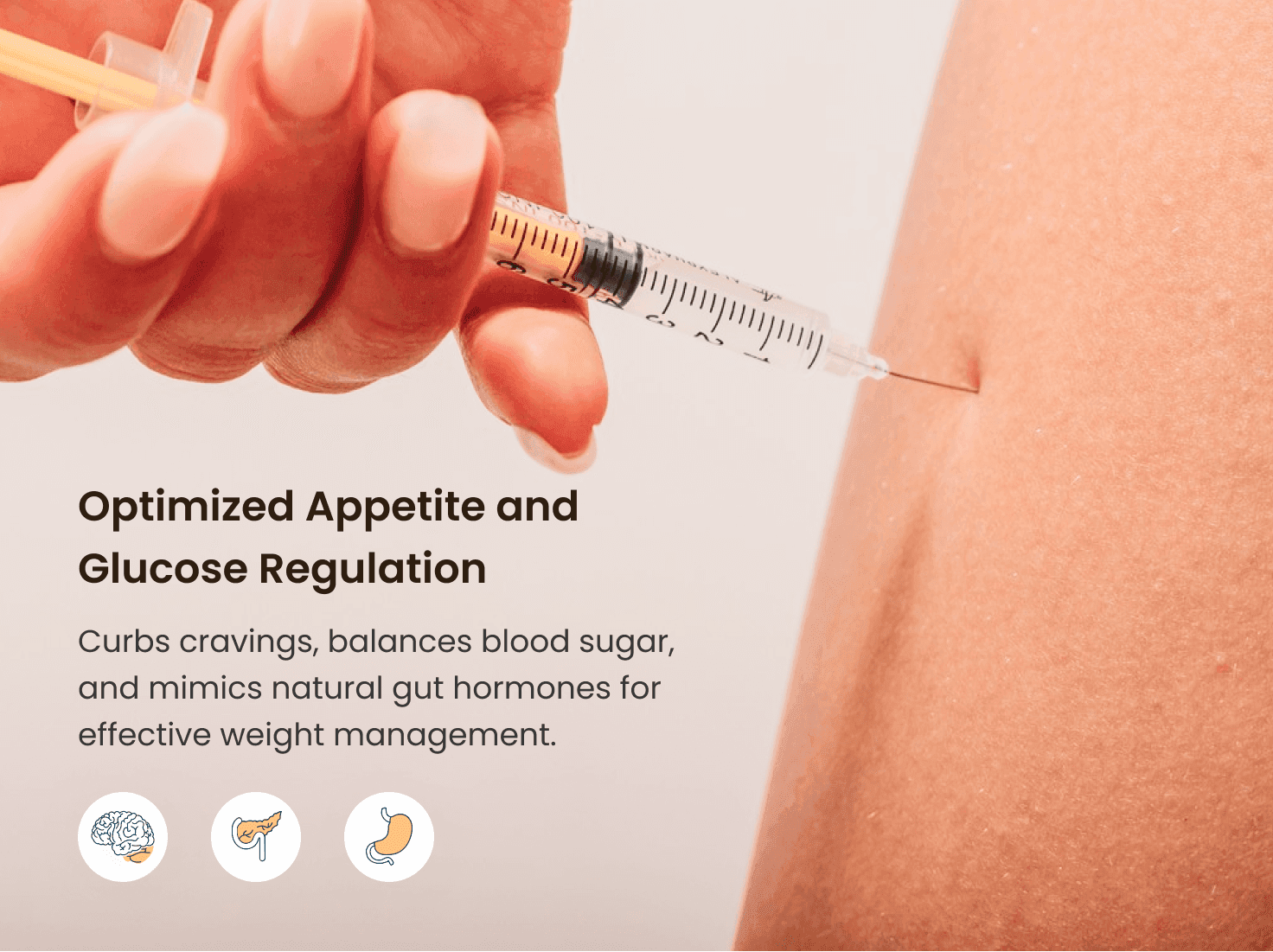
Getting started : Semaglutide Dosing Schedule
For safe and effective use, semaglutide is introduced gradually. This helps the body adjust to the medication and reduces the likelihood of side effects.
Week 1 to Week 4: 0.25 mg
Week 5 to Week 8: 0.5 mg
Week 9 to Week 12: 1 mg
Week 13 to Week 16: 1.7 mg
Below is an image of the semaglutide weight loss dosage chart.

Long-Term Maintenance Dose
Once your body has adjusted to the medication, a maintenance dose is established to help sustain weight loss.
Week 17 and onward: 2.4 mg injected subcutaneously once per week
Adjusting the Dose: What to Consider
Not everyone responds to the dosage increase in the same way. If you experience difficulty tolerating the dose escalation, adjustments may be needed.
If you cannot tolerate a higher dose, delay the dose increase by 4 weeks.
If you are unable to tolerate the 2.4 mg maintenance dose, you can reduce it to 1.7 mg per week for up to 4 weeks. After this, attempt to increase the dose back to 2.4 mg. If this dose still isn’t tolerable, discontinue treatment.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors can influence how semaglutide is absorbed and processed in the body, affecting both the starting dose and the maintenance dose.
Disease: If you have type 2 diabetes, your blood glucose levels should be monitored both at the start and throughout the treatment.
Genetics: Factors like body mass and build can affect how the drug is distributed throughout the body.
Age: Aging, particularly impaired kidney function, can slow drug excretion and increase the risk of toxicity.
Diet: Past and present food and drug interactions may affect how semaglutide is processed in the body.
Sex: The way semaglutide metabolizes depends on the biological sex of the individual.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy can cause maternal toxicity, potentially harming the fetus.
Sleep schedule: Administering medications at the wrong time of day can lead to unwanted effects.
Other factors :
Do not take semaglutide with any other semaglutide-containing drugs or GLP-1 receptor agonists.
The safety and effectiveness of using semaglutide along with other weight-loss medications have not been established.
This drug has not been studied in people with a history of pancreatitis.
Importance of Medical Supervision
Starting your semaglutide treatment is a positive step toward weight management, but it’s essential to have ongoing medical supervision. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals ensure that you’re on track to meet your weight loss goals and help prevent complications.
Medical supervision is particularly important because certain medications can interact with semaglutide. For example, when taken with insulin or an insulin secretagogue, semaglutide can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Your healthcare provider may need to adjust your insulin dosage to reduce this risk.
It’s also crucial not to alter your semaglutide dosage without medical guidance. While it may be tempting to increase the dose for faster results, doing so could lead to severe side effects or reduce the effectiveness of the treatment. Your healthcare provider’s expertise helps ensure your weight loss journey remains safe and effective.
Key Guidelines to Remember
Monitor your blood sugar levels if you have type 2 diabetes, especially during treatment.
Do not use semaglutide in combination with other semaglutide-containing products or GLP-1 receptor agonists.
The safety and effectiveness of combining semaglutide with other weight loss medications have not been established.
Semaglutide has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis.
Uses of Semaglutide for Weight Management
Semaglutide is approved for use as part of a comprehensive weight management plan, which includes a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. It is prescribed for:
Adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m² or higher (obesity)
Adults with a BMI of 27 kg/m² or higher (overweight), along with at least one weight-related condition such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia
Current version
Oct 3, 2024
Written by
Leah Bush (Acute Care Nurse Practitioner)
Fact checked by
Dr. Joel Lopez (MD, CNS, DABAARM)
Lose weight effectively
with GLP-1s
Fill out a quick form to share your
medical history, helping us tailor the
perfect plan for you.

Semaglutide Weight Loss Dosage Chart: A Comprehensive Guide
Semaglutide

Leah Bush
•
5 mins read
• Oct 3, 2024
Compounded Semaglutide is a popular medication used to support long-term weight management in adults, especially those dealing with obesity or weight-related health conditions like hypertension or type 2 diabetes. To achieve the best results and minimize side effects, it’s important to follow a carefully structured dosing schedule. This blog will guide you through the recommended dose escalation, maintenance strategies, and key considerations to help ensure safe and effective use of semaglutide for weight loss.
Getting started : Semaglutide Dosing Schedule
For safe and effective use, semaglutide is introduced gradually. This helps the body adjust to the medication and reduces the likelihood of side effects.
Week 1 to Week 4: 0.25 mg
Week 5 to Week 8: 0.5 mg
Week 9 to Week 12: 1 mg
Week 13 to Week 16: 1.7 mg
Below is an image of the semaglutide weight loss dosage chart.
Long-Term Maintenance Dose
Once your body has adjusted to the medication, a maintenance dose is established to help sustain weight loss.
Week 17 and onward: 2.4 mg injected subcutaneously once per week
Adjusting the Dose: What to Consider
Not everyone responds to the dosage increase in the same way. If you experience difficulty tolerating the dose escalation, adjustments may be needed.
If you cannot tolerate a higher dose, delay the dose increase by 4 weeks.
If you are unable to tolerate the 2.4 mg maintenance dose, you can reduce it to 1.7 mg per week for up to 4 weeks. After this, attempt to increase the dose back to 2.4 mg. If this dose still isn’t tolerable, discontinue treatment.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several factors can influence how semaglutide is absorbed and processed in the body, affecting both the starting dose and the maintenance dose.
Disease: If you have type 2 diabetes, your blood glucose levels should be monitored both at the start and throughout the treatment.
Genetics: Factors like body mass and build can affect how the drug is distributed throughout the body.
Age: Aging, particularly impaired kidney function, can slow drug excretion and increase the risk of toxicity.
Diet: Past and present food and drug interactions may affect how semaglutide is processed in the body.
Sex: The way semaglutide metabolizes depends on the biological sex of the individual.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy can cause maternal toxicity, potentially harming the fetus.
Sleep schedule: Administering medications at the wrong time of day can lead to unwanted effects.
Other factors :
Do not take semaglutide with any other semaglutide-containing drugs or GLP-1 receptor agonists.
The safety and effectiveness of using semaglutide along with other weight-loss medications have not been established.
This drug has not been studied in people with a history of pancreatitis.
Importance of Medical Supervision
Starting your semaglutide treatment is a positive step toward weight management, but it’s essential to have ongoing medical supervision. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals ensure that you’re on track to meet your weight loss goals and help prevent complications.
Medical supervision is particularly important because certain medications can interact with semaglutide. For example, when taken with insulin or an insulin secretagogue, semaglutide can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Your healthcare provider may need to adjust your insulin dosage to reduce this risk.
It’s also crucial not to alter your semaglutide dosage without medical guidance. While it may be tempting to increase the dose for faster results, doing so could lead to severe side effects or reduce the effectiveness of the treatment. Your healthcare provider’s expertise helps ensure your weight loss journey remains safe and effective.
Key Guidelines to Remember
Monitor your blood sugar levels if you have type 2 diabetes, especially during treatment.
Do not use semaglutide in combination with other semaglutide-containing products or GLP-1 receptor agonists.
The safety and effectiveness of combining semaglutide with other weight loss medications have not been established.
Semaglutide has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis.
Uses of Semaglutide for Weight Management
Semaglutide is approved for use as part of a comprehensive weight management plan, which includes a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. It is prescribed for:
Adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m² or higher (obesity)
Adults with a BMI of 27 kg/m² or higher (overweight), along with at least one weight-related condition such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, or dyslipidemia



Current version
Oct 3, 2024
Written by
Leah Bush (Acute Care Nurse Practitioner)
Fact checked by
Dr. Joel Lopez (MD, CNS, DABAARM)
Lose weight effectively
with GLP-1s
Fill out a quick form to share your
medical history, helping us tailor the
perfect plan for you.

Lose weight effectively
with GLP-1s
Fill out a quick form to share your
medical history, helping us tailor the
perfect plan for you.
